Hierarchical Structure of India's Defence Forces : A System of Order and Equivalence
The Indian Armed Forces, a formidable institution safeguarding the nation's sovereignty, operate under a meticulously defined hierarchical structure. This structure is not merely a formality but a critical component ensuring operational efficiency, clear lines of command, and seamless coordination across the Army, Navy, and Air Force.
1. The Indian Army 🇮🇳💂: The Dominant Land Force
The Indian Army, the largest component of the Indian Armed Forces, boasts a complex ranking system that reflects its size and operational scope.
- Commissioned Officers:
- These officers, appointed by the President of India, are the intellectual and strategic backbone of the Army.
- The hierarchy begins with the entry-level rank of Lieutenant, progresses through stages of increasing responsibility, and culminates in the highest active rank of General.
- Key ranks include:
- General: The Chief of the Army Staff (COAS), the highest-ranking officer in the Indian Army.
- Lieutenant General: Commands corps-level formations and holds significant administrative responsibilities.
- Major General: Commands divisions, a substantial operational unit.
- Brigadier: Commands brigades, a smaller but crucial operational formation.
- Colonel: Commands battalions or regiments.
- Lieutenant Colonel: Second-in-command of a battalion or regiment.
- Major: Holds key staff and command appointments.
- Captain: Commands companies or equivalent sub-units.
- Lieutenant: The entry-level commissioned officer.
- Field Marshal: An honorary five-star rank bestowed for exceptional wartime service. Only two officers have been awarded this rank.
- Junior Commissioned Officers (JCOs):
- JCOs form a vital link between commissioned officers and other ranks, providing experience and guidance.
- Ranks include:
- Subedar Major: The senior-most JCO in a unit.
- Subedar: Holds key leadership and administrative roles.
- Naib Subedar: Assists in leadership and operational tasks.
- Other Ranks:
- This category comprises the bulk of the Army's personnel, carrying out the core operational tasks.
- Ranks include:
- Havildar: Commands sections or small teams.
- Naik: Assists in team leadership.
- Lance Naik: A junior non-commissioned rank.
- Sepoy: The basic rank of a soldier.
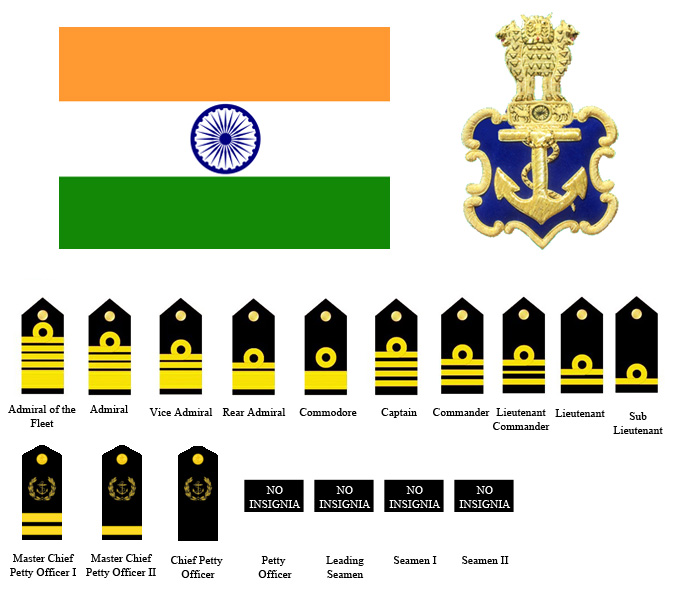
The Indian Navy's ranking structure is designed to reflect its specialized maritime operations and naval traditions.
- Commissioned Officers:
- Naval officers, also commissioned by the President, navigate a hierarchy that reflects their increasing expertise and command responsibilities.
- Key ranks include:
- Admiral: The Chief of the Naval Staff (CNS), the highest-ranking officer in the Indian Navy.
- Vice Admiral: Commands fleets or major naval commands.
- Rear Admiral: Commands flotillas or naval bases.
- Commodore: Commands squadrons or naval establishments.
- Captain: Commands major warships.
- Commander: Commands smaller warships or holds key staff roles.
- Lieutenant Commander: Senior officer on smaller ships or in departments.
- Lieutenant: Officer of the watch, department officer on larger ships.
- Sub-Lieutenant: Entry level officer.
- Admiral of the Fleet: An honorary five-star rank, rarely awarded.
- Personnel Below Officer Rank (PBOR):
- This category includes highly skilled sailors and technicians.
- Ranks include:
- Master Chief Petty Officer I & II: Senior-most sailors, holding crucial technical and leadership roles.
- Chief Petty Officer: Holds significant technical and supervisory responsibilities.
- Petty Officer: Skilled sailor, responsible for specific tasks.
- Leading Seaman: Experienced sailor.
- Seaman I & II: Entry level sailors.
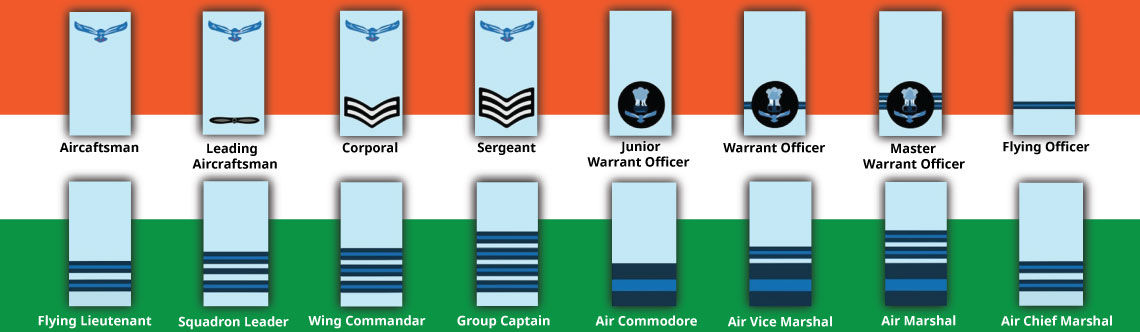
3. The Indian Air Force 🇮🇳✈️: The Aerial Guardians
The Indian Air Force's ranking structure is tailored to its complex aerial operations and technological requirements.
- Commissioned Officers:
- Air Force officers, commissioned by the President, progress through a hierarchy that reflects their flying skills and command responsibilities.
- Key ranks include:
- Air Chief Marshal: The Chief of the Air Staff (CAS), the highest-ranking officer in the Indian Air Force.
- Air Marshal: Commands air commands.
- Air Vice Marshal: Commands air bases or operational units.
- Air Commodore: Commands squadrons or air stations.
- Group Captain: Commands wings or major units.
- Wing Commander: Commands squadrons or smaller units.
- Squadron Leader: Holds key operational and administrative roles.
- Flight Lieutenant: Experienced pilot or navigator.
- Flying Officer: Entry level officers.
- Marshal of the Indian Air Force: An honorary five-star rank, awarded for exceptional service.
- Airmen:
- This category includes skilled technicians and support personnel.
- Ranks include:
- Master Warrant Officer: Senior-most airmen, holding crucial technical and administrative roles.
- Warrant Officer: Holds significant technical and supervisory responsibilities.
- Junior Warrant Officer: Skilled technician.
- Sergeant: Holds technical and supervisory roles.
- Corporal: Skilled technician.
- Leading Aircraftsman: Experienced airman.
- Aircraftsman: Entry level airman.
Equivalence and Inter-Service Coordination 🤝: A Unified Force
The Indian Defence Forces maintain a system of rank equivalence, ensuring seamless coordination during joint operations and inter-service interactions.
- A General in the Army is equivalent to an Admiral in the Navy and an Air Chief Marshal in the Air Force.
- This equivalence facilitates efficient communication and command during joint operations, reflecting the unified nature of the Indian Defence Forces.